Pesticide wastewater pretreatment technology
- release date: 2025-11-20 15:53:38
- author: Hongtai Huairui
- Reading: 881
- key words: pesticide wastewater
The main reason for the low treatment rate and compliance rate of pesticide wastewater is that pesticide production wastewater is a kind of wastewater that is difficult to treat. Pesticide wastewater not only has high and complex pollutant content, poor biodegradability, but also often contains biological toxic substances, and some wastewater contains high salinity, high ammonia nitrogen, high phosphorus content, high fluorine content, etc., and requires a large amount of environmental protection capital investment to meet the standards. Therefore, seeking some representative and economical process and technology routes for treating pesticide wastewater is the key to solving pesticide wastewater pollution. For the production of wastewater of different properties, its treatment technology is also diverse, and it is impossible to treat the wastewater of all pesticide enterprises with a single technology, but for wastewater with some commonalities, its treatment technology can be summarized and summarized, and has universal applicability. For some common wastewater, it must be strictly collected separately and pretreated separately, which is also the basic method of treating such wastewater.
The enterprises introduced in this article produce ammochloropyridic acid, glufosinate, chlorofluoropyroacetate and preparation products, which are typical pesticide production enterprises. In the production process, classified collection and individual pretreatment are strictly implemented, focusing on the treatment methods and effects, in order to have reference and guiding significance for similar production enterprises.
1. High ammonia nitrogen wastewater
In the process of producing ammochloropyridic acid, according to its production raw materials and processes, the hydrolyzed mother liquor wastewater produced by the hydrolysis process of ammochloropicridic acid intermediate tetrachloropicolinic acid contains a large amount of ammonium sulfate in the wastewater, resulting in a particularly high concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the discharged wastewater. Using the principle that NH4+ combines with OH to produce NH3•H2O under alkaline conditions, and then blows off this part of hydrated ammonia to reduce the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater, the gas method is used to treat high concentration of ammonia nitrogen, which is also the most commonly used treatment method for treating high ammonia nitrogen wastewater. Therefore, these two streams of wastewater are collected separately and pretreated separately using different technologies. The processing process is shown in Figure 1.
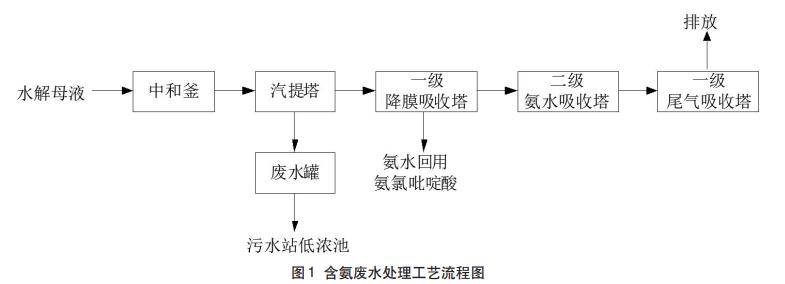
There are 2 sets of stripping treatment units with a wastewater volume of 5t/h, treating 200m3 of high ammonia nitrogen wastewater per day, and the ammonia nitrogen removal rate of the gas tower reaches more than 85%, the average ammonia nitrogen in the influent is 1000mg/L, and the ammonia nitrogen concentration in the effluent is 100-150mg/L after gas pretreatment.
2. High fluorine wastewater
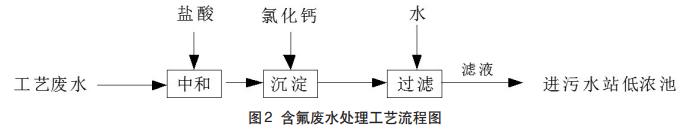
The most simple and efficient fluoride removal method is to use Ca2+ and F to generate CaF2 precipitation and remove it. Generally, Ca2+ is provided by adding Ca(OH)2 or CaCl2, Ca(OH)2 has low cost but small solubility, and when treating high-fluoride wastewater, it is limited by the Ca2+ concentration provided, and the removal efficiency is not ideal. The wastewater with high fluorine content is 10m3 per day, the design treatment capacity of wastewater is 10m3/d, the removal rate of fluoride ions can reach 88.5%, and the treated fluoride ion concentration is about 200mg/L. (See Figure 2)
3. Pretreatment of high-salt wastewater
In a high-salinity environment, the dehydrogenase activity of microorganisms decreases, and the osmotic pressure of water increases with the increase of salt concentration, which dehydrates microbial cells and causes cell protoplasm separation, which is not conducive to the growth of microorganisms. Therefore, high-salt wastewater must be desalinated before entering the biochemical treatment unit. The wastewater treatment process with high salt content of the enterprise adopts secondary evaporation desalination. At present, there are two sets of secondary evaporation systems under construction, with a design processing capacity of 240m3/d. The device is mainly used to treat ammonium sulfate recovery wastewater from amlopyridic acid and xylene washing wastewater from glufosinate crude diester. After desalination treatment, the salt removal rate of wastewater is more than 90%, ensuring that the wastewater can be biochemically treated.
4. Fenton oxidation pretreatment
In the process of pesticide production, some high-concentration process wastewater will be generated, such as concentrated sewage from secondary evaporation system, concentrated sewage from distillation towers, neutralization distillation wastewater from glufosinate ammonium tetrahydrofuran, acid distillation distillation wastewater, ethanol distillation recycling wastewater, chlorofluoropyrioxyacetate distillation and recycling wastewater, distillation vacuum pump wastewater, etc. These wastewaters are characterized by high COD, low BOD, and contain large amounts of non-biodegradable polymeric organic matter. For this part of wastewater, advanced oxidation treatment is usually used to oxidize organic matter such as long chains and ring chains to generate organic matter that is easily biodegradable with broken chains, and then biochemically treated. At present, the company has built a Fenton oxidation plant with a treatment capacity of 600m3/d, which is used to pretreat high-concentration wastewater and improve the biodegradability of wastewater. Fenton oxidation can remove about 30% of COD, and although the removal rate is not high, the B/C increases from 0.08 to 0.45, which greatly improves the biochemistry and is conducive to further biodegradation.
5. Comprehensive wastewater biochemical treatment
After the wastewater is pretreated, it finally enters the biochemical conditioning tank, where it is mixed with other production wastewater for biochemical treatment. The quality and quantity of wastewater in the whole plant are shown in Table 1.
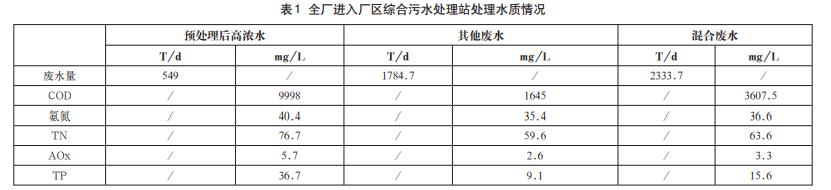
The comprehensive wastewater treatment process in the plant adopts the A2/O process, and after a long period of operation, the concentrations of COD, ammonia nitrogen and TP at the outlet of the secondary sedimentation tank after treatment by the sewage station are about 361mg/L, 15mg/L, and 8mg/L. After the wastewater with special properties is pretreated, it is mixed with other wastewater and biochemically treated, and the enterprise achieves standard pipe discharge.
6. Conclusion
Pesticide wastewater treatment is difficult, and the key is that the pretreatment of wastewater with special properties must be done well, otherwise it will directly affect the final biochemical treatment process. Therefore, the more types there are, the more difficult it is to treat wastewater, and separate collection and pretreatment are the key. In the pretreatment of high ammonia nitrogen wastewater, fluorine wastewater, high salt wastewater and wastewater with poor biochemical properties, the pretreatment methods of stripping, calcium chloride precipitation, multi-effect evaporation and Fenton oxidation are proposed, and good pretreatment results are achieved. After biochemical treatment with other wastewater, it can meet the sodium pipe standard.





 hthrjt2017@gmail.com
hthrjt2017@gmail.com















