01 Hazards of landfill leachate and characteristics of membrane landfill leachate treatment
Landfill leachate has the characteristics of high concentration of toxic and harmful substances, complex composition, high content of organic matter, large fluctuations in water quality and quantity, and difficulty in treatment, which is very harmful to the environment. At present, the main methods of treating landfill leachate are: incorporating into urban sewage treatment plants, landfill recycling, incineration to waste incineration power plants, waste reprocessing, etc. The membrane process is more and more used in the treatment of landfill leachate due to its simple equipment, easy operation, and good effluent quality.
02 Introduction to common membrane treatment processes
At present, the common membrane landfill leachate treatment process is mainly biochemical (A/O or A2/O) + MBR/tubular ultrafiltration + nanofiltration + reverse osmosis (+DTRO). In the common membrane landfill leachate treatment process, the main functions of each process are as follows:
(1) Non-membrane processes (such as traditional biochemical methods or some anaerobic/aerobic reactors, etc.) are usually used as pretreatment processes for membrane processes;
(2) MBR: The MBR process is the core of the entire landfill leachate treatment system and is one of the main bodies of removing organic matter from the landfill leachate. At present, the common MBR membrane modules mainly include plate membrane modules and hollow fiber membrane modules, the two MBR modules have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the plate MBR membrane modules have the advantages of low transmembrane pressure difference, higher sludge concentration, lower pretreatment requirements, lower maintenance and cleaning frequency, no need for backwashing, and relatively simple operation compared with hollow fiber membrane modules. Hollow fiber MBR membrane modules have the advantages of relatively high loading density, small membrane pool footprint, and low investment in membrane module equipment. The higher the concentration of activated sludge in the MBR membrane tank under the same sludge load, the stronger its ability to treat organic matter.
(3) Ultrafiltration: Due to its high filtration accuracy, ultrafiltration can separate the microbial bacteria and sediments brought by the biochemical part from the sewage, and ultrafiltration can also remove some organic matter with large molecular weight in the wastewater. The water entering the ultrafiltration process often has high turbidity, color, COD and heavy taste, so ultrafiltration (common tubular ultrafiltration) in the landfill leachate treatment process is used as a pretreatment for NF and RO, which can further remove impurities in the water and ensure the stable operation of the subsequent process.
(4) Nanofiltration: The main pollutants in MBR or ultrafiltration process water are usually organic matter, microorganisms, hardness, alkalinity and heavy metals. The nanofiltration process can remove most of the organic matter and polyvalent inorganic salts in the MBR or ultrafiltration process produced water, and its production water can basically meet the discharge standards. The concentrated water of the nanofiltration process is generally returned to the landfill or further evaporated for treatment; At present, the recovery rate of nanofiltration system in the treatment of landfill leachate is generally relatively high (80%~85%), and the content of organic matter in the influent is high, which leads to the biggest problem faced by nanofiltration is membrane pollution and scaling. The lifespan of the membrane elements treated with landfill leachate is often low. As far as some landfill leachate treatment projects have been understood, the water quality of most of the nanofiltration process water cannot meet the requirements of reverse osmosis influenza, and generally has a high color and unpleasant taste, and the treatment effect is not ideal.
(5) Reverse osmosis process mainly plays a role in reducing the conductivity and organic matter content of external drainage in the leachate treatment process, in addition, the reverse osmosis process can greatly intercept ionized nitrogen (such as nitrate, etc.) in the landfill leachate, reduce the total nitrogen value in the produced water, and finally make the discharged water below the national discharge standard. As far as we know about the use of reverse osmosis at the landfill leachate treatment site, there are mainly the following problems:
a. Concentrated water reflux increases system recovery: Reverse osmosis or nanofiltration processes often consider the method of concentrated water reflux to improve the system recovery rate, and many landfill leachate treatment systems also use the nanofiltration or reverse osmosis process of two-stage concentrated water reflux.
b. The use of in-section circulation booster pump: In the landfill leachate treatment site that has been understood, many reverse osmosis treatment systems have set up a single-stage concentrated water return (that is, the concentrated water in each section is circulated inside the section through the intra-section circulation booster pump, and the circulation volume in the section is several times the inlet water volume of the reverse osmosis system), which can increase the flow rate on the inlet side of the membrane element and prevent pollutants from being deposited to pollute the membrane element, but the large amount of concentrated water will lead to the deterioration of the influent water quality of the section, thereby aggravating the membrane pollution. In landfill leachate systems with poor water quality, backflow can lead to frequent membrane cleaning, which can affect membrane element life.
c. Instrumentation problems: Due to the fact that landfill leachate items are generally small, two-stage design is often used to improve recovery rate. However, in the landfill leachate projects we investigated on site, there are often problems with the monitoring data of some systems, such as the two-stage system only sets up influent water and concentrated water pressure gauges, and the pressure between sections cannot be monitored; Or the circulation booster pump in the single membrane shell is set up, but the pressure and conductivity of the membrane shell cannot be detected, which will cause the failure of the membrane system to be found in time during operation, and eventually lead to serious pollution or damage to the membrane elements.
d. DTRO: The main function of DTRO is to further reduce the discharge of concentrated water in the system, but it will also cause a further increase in the concentration of circulating water.
03 Domestic Waste Landfill Pollution Control Standard (GB 16889-2008)
Some landfills use membrane method to remove organic matter in leachate to solve the problem of COD emissions not meeting the standard during leachate treatment. The domestic waste landfill pollution control standard (GB 16889-2008) formulated by our country makes relevant provisions on pollutant emissions, refer to Table 1:

04 Introduction to landfill failures
The following is a combination of two typical fault cases to introduce the main problems faced by the reverse osmosis system of the landfill project, refer to Table 2:
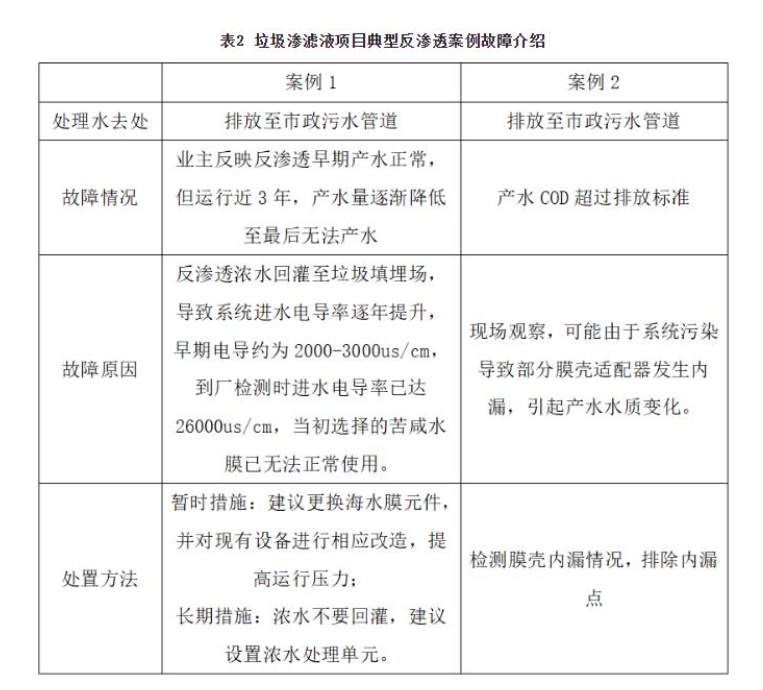
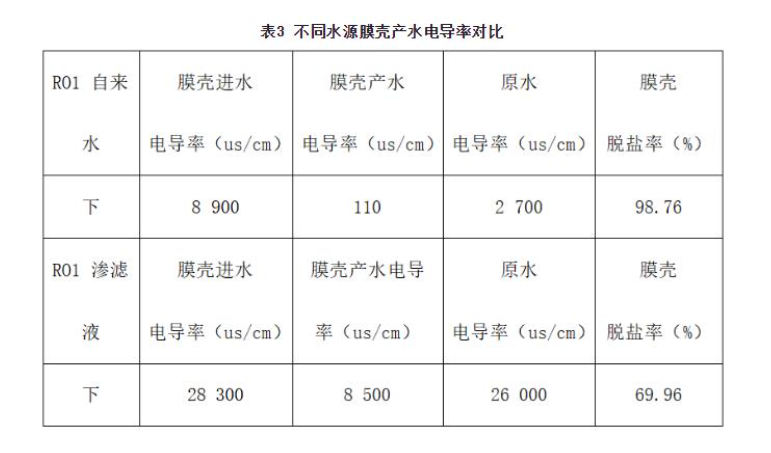
Case 1 is a typical case where the membrane system cannot operate normally due to recharge during landfill leachate treatment. This kind of situation often occurs in landfill leachate projects where the treated concentrated water cannot be discharged or treated, and the final result is often due to the high salt content of the influent water, resulting in the inability of the reverse osmosis membrane system to continue to operate, and this process can generally be seen in about 2~3 years. In addition, according to the field investigation, when the water source with conductivity of 2000~3000us/cm was used to simulate the initial design of reverse osmosis influent, the conductivity and water yield of reverse osmosis produced water were basically normal, but the desalination rate was greatly reduced after switching to landfill leachate (see Table 3).
In addition, during the investigation of case 1, it was found that when landfill leachate was used as water inlet, the water production conductivity of the membrane shell at the same position increased rapidly over time, as shown in Table 4:

Due to the low water yield, the water yield of each membrane shell can no longer be displayed on the flowmeter (that is, the water yield does not reach the minimum limit of the flowmeter), and the conductivity of the single membrane shell water produced by each shell water production sampling tube increases rapidly with time, which indicates that the concentration polarization occurs on the membrane surface, resulting in a rapid increase in the conductivity of the water production.
In the subsequent test results of the membrane element performance, we found that although it has been used for nearly 3 years and there are many traces of contamination in appearance, the decay of the desalination rate of the membrane element under the standard evaluation conditions is not very prominent. Refer to the table below (Table 5):

Case 2 can be regarded as a typical case of reverse osmosis failure, due to improper installation of the new system or the high pressure difference of the reverse osmosis system, the internal leakage problem between the membrane elements and the connectors in part of the membrane shell occurs, resulting in the deterioration of the water quality of the membrane shell, thus affecting the overall water quality.
05 Landfill fault analysis and improvement suggestions
Through on-site investigation, we found that the landfill plant membrane leachate treatment project has the following problems:
(1) The membrane is polluted quickly, cleaning is frequent, there are many operating failures, and the life of the membrane element is generally short.
(2) The corrosion of equipment, pipelines and instruments is serious.
(3) Concentrated water recharge leads to an increase in the salinity content of the influent year by year, which ultimately makes the reverse osmosis membrane system difficult to operate.
(4) The return of concentrated water in the reverse osmosis system itself is also an important reason for the low life of the membrane elements of the landfill leachate project.
(5) On-site instrument settings often cannot meet the needs of equipment operation monitoring.
Judging from the current survey results of landfill operation projects, the following improvements need to be considered:
(1) Timely detection and replacement of equipment and instruments to ensure the accuracy of system monitoring data;
(2) For projects that cannot discharge concentrated water, the evaporation and crystallization method can be considered to convert high-concentration wastewater into solid waste treatment. If there is a waste incineration project in the future, the final concentrated water can be incinerated in the incinerator.
(3) Timely chemical cleaning, if the system performance cannot be restored, consider changing the membrane element to ensure that the water quality of each section is qualified.
(4) For the system that cannot work normally due to the high salt content of the influent due to recharge, it is possible to consider using seawater membrane or high-pressure reverse osmosis membrane elements to replace the original brackish water membrane elements, but the choice of this scheme requires consideration of the corresponding modification of the existing equipment, such as: replacing the high-pressure pump to a higher head, a higher level of pressure resistance pipeline, whether the existing instrument range matches the excessive salt content, whether the existing agent can play a role under new working conditions, whether it needs to be replaced with a new type of agent, etc., and, This scheme can only be effective for a certain period of time, and with the continuous recharge of the concentrate, the reverse osmosis influent water continues to circulate and concentrate, which will eventually lead to high salt content and the inability of the reverse osmosis system to operate. Therefore, to solve the problem of circulating liquid concentration, it is necessary to consider transporting it or converting it into a solid waste discharge system, rather than unlimited circulation and concentration within the system.
(5) Advanced oxidation technology can be considered to treat reverse osmosis or nanofiltration concentrated water to reduce the organic matter content in the recharge water or subsequent evaporation crystallization influent.
06 Outlook and Reflection
With the emergence of waste-to-energy plant projects in various places, the leachate membrane method can solve the problem of concentrated water discharge in landfills to a certain extent. In addition, for recharge water with high concentration of organic matter and good biochemical performance, can anaerobic process be considered to further recycle organic matter and turn it into treasure? In any case, there are still many problems in the landfill leachate treatment process that need to be discovered and solved.
























