The difference between membrane water treatment and traditional water treatment
The use of membrane technology can greatly improve the quality of produced water. According to the treatment depth, sewage treatment can be divided into primary treatment, secondary treatment and deep treatment. The main purpose of primary treatment is to remove suspended solids, often using physical methods, and the removal rate of BOD5 is generally 20%~30%; The purpose of secondary treatment is to further remove colloids and dissolved pollutants from sewage, and the removal rate of BOD5 is more than 90%. Deep treatment is intended to meet higher treatment and discharge requirements or wastewater reuse.
Membrane technology is usually used to treat secondary treatment activated sludge effluent, or the membrane treatment system is directly placed in the biochemical tank to replace the original secondary sedimentation tank, flocculation sedimentation tank and other links. After using membrane technology, the traditional sewage treatment process can directly produce high-quality reclaimed water.
6 commonly used membrane treatment technologies
1. Microfiltration (MF) membrane technology
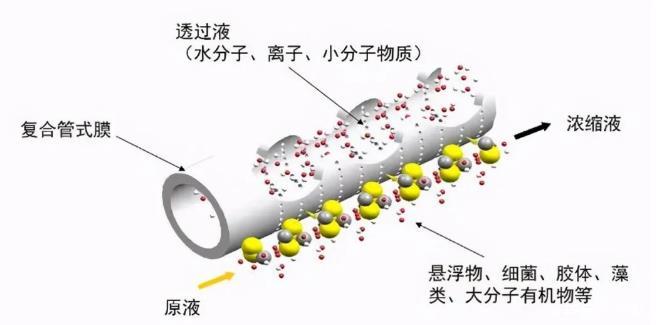
1. The basic principle of microfiltration (MF).
The microfiltration membrane can trap particles between 0.1 and 1 microns. Microfiltration membranes allow macromolecules and dissolved solids (inorganic salts) to pass through, but they can trap suspended solids, bacteria, and large molecular weight colloids. The operating pressure of the microfiltration membrane is generally 0.3-7bar. Microfiltration membrane filtration is the earliest membrane technology developed and applied in the world, using natural or artificially synthesized polymer compounds as membrane materials. For microfiltration membranes, the separation mechanism is mainly screening and interception.
2. Application of microfiltration membrane
(1) Water treatment industry: removal of suspended solids, microscopic particles and bacteria in water;
(2) Electronics industry: ultrapure water in the semiconductor industry, integrated circuit cleaning water terminal treatment;
(3) Pharmaceutical industry: medical pure water sterilization, pyrogen removal, drug sterilization;
(4) Medical industry: remove bacteria in various solutions such as tissue fluid, antimicrobials, serum, plasma protein, etc.;
(5) Food industry: removal of suspended matter, microorganisms and odor impurities, yeast and mold in beverages, alcohol, soy sauce, vinegar and other foods, clarification and filtration of juice.
(6) Chemical industry: filtration and clarification of various chemicals.
2. Ultrafiltration (UF) membrane technology
 1、超滤(UF)原理
1、超滤(UF)原理
Ultrafiltration (UF) principle
Ultra-filtration (UF) is a membrane separation technology that purifies and separates solutions. The ultrafiltration membrane system is a solution separation device that uses ultrafiltration membrane filaments as the filter medium and the pressure difference between the two sides of the membrane as the driving force. The ultrafiltration membrane only allows solvents (such as water molecules), inorganic salts and small molecules of organic matter in the solution to pass through, while the suspended solids, colloids, proteins and microorganisms in the solution are trapped to achieve the purpose of purification and separation.
The range of ultrafiltration pore size and molecular weight cut-off has always been vaguely defined, and it is generally believed that the filtration pore size of ultrafiltration membrane is 0.001-0.1 microns, and the molecular weigh cut-off (MWCO) is 1,000-1,000,000 Dalton. Strictly speaking, ultrafiltration membranes have a filtration pore size of 0.001-0.01 microns and a molecular weight of 1,000-300,000 Dalton. Microporous membranes with a filtration pore size greater than 0.01 microns or a molecular weight greater than 300,000 Dalton should be defined as microfiltration membranes or fine filtration membranes.
2. Application of ultrafiltration membrane
The application range of ultrafiltration membrane is extremely wide, basically the industries involved in filtration can use filtration equipment, the basic filtration industries are as follows:
As the terminal treatment of reverse osmosis pretreatment and ultrapure water in the preparation process of pure water and ultrapure water; It is used in industrial water to separate bacteria, heat sources, colloids, suspended impurities and macromolecular organic matter; drinking water and mineral water purification; Concentration, purification and clarification of fermentation, enzyme preparation industry and pharmaceutical industry; Juice concentration and separation; separation, concentration and clarification of soybeans, dairy, sugar industry, wine, tea, vinegar, etc.; purification and recycling of industrial wastewater and domestic sewage; Recycling of electrophoretic paints.
Ultrafiltration membrane separation can replace natural sedimentation, plate and frame filtration, vacuum drum, centrifugal separation, solvent extraction, resin purification, activated carbon decolorization and other processes in traditional processes. The process is operated at room temperature, with no phase change and no secondary pollution.
3. Nanofiltration (NF) membrane technology

1. Nanofiltration (NF) principle
Nanofiltration (NF) is a new molecular-level membrane separation technology, which is currently one of the research hotspots in the field of membrane separation in the world. NF film pore size is above 1nm, generally 1-2nm; The retention performance of solutes was between RO and UF membranes. RO membranes have high removal rates for almost all solutes, but NF membranes have high removal rates for only specific solutes. NF membranes can remove divalent and trivalent ions, organic matter of Mn≥200, as well as microorganisms, colloids, heat sources, viruses, etc.
A major feature of nanofiltration membrane is that the membrane body is charged, which is an important reason why it still has high desalination performance at very low pressure (only 0.5MPa) and can remove inorganic salts even with membranes with a retention molecular weight of hundreds of membranes, and is also the main reason for the low operating cost of NF.
NF is suitable for all kinds of saline water sources, the water utilization rate is generally 75%~85%, and the seawater desalination is 30%~50%, and there is no acid and alkali wastewater discharge.
2. Application of nanofiltration membrane in water treatment
(1) Application of nanofiltration membrane in drinking water: nanofiltration has low operating pressure and is the preferred process for drinking water preparation and deep purification.
At present, the water supply sources in most cities are polluted to varying degrees, and the conventional treatment process of waterworks does not have a high removal rate of organic matter in the water. Peltier et al.'s four-year follow-up study showed that the DOC in the water was reduced to an average of 0.7 mgC/L, the residual chlorine content in the effluent was reduced from 0.35 mg/L to 0.1 mg/L, and the formation of trihalomethanes (THMs) in the final network cable was reduced by 50% compared with that without the nanofiltration system. In addition, the biostability of the water produced is improved due to the reduction of biodegradable dissolved organic carbon (BCOD).
Nanofiltration technology can remove most of the Ca and Mg ions, so desalting is the most used field of nanofiltration technology. Membrane water treatment technology is similar to the conventional lime softening and ion exchange process in terms of investment, operation, maintenance and price, but has the advantages of no sludge, no regeneration, complete removal of suspended solids and organic matter, easy operation and saving footprint, and there are many application examples. Nanofiltration can be directly used for the softening of groundwater, surface water and wastewater, and can also be used as a pretreatment for reverse osmosis, solar photovoltaic desalination units, etc.
(2) Application of nanofiltration membrane in seawater desalination: Seawater desalination refers to desalination of seawater with a salt content of 35000mg/L to drinking water below 500mg/L.
(3) Application of nanofiltration membrane in wastewater treatment:
(1) Domestic sewage: Domestic sewage is generally treated with a combination of biodegradation/chemical oxidation methods, but the amount of oxidant is too large, there are many residues, and the water quality of ultrafiltration can meet the water requirements of reuse to hotel toilet flushing, greening and other links, and the water quality of nanofiltrated water can meet the sanitary standard of drinking water (GB5749.85), which can be reused to hotel laundry, bathing and other links with higher water requirements.
(2) Textile, printing and dyeing wastewater: The dyes contained in textile wastewater are difficult to remove by biological methods, and the concentration, pressure, total dissolved solids and inorganic salt content of acidic, active, direct and disperse dye aqueous solutions may affect the retention performance of nanofiltration membranes.
(3) Tanning wastewater: Tanning wastewater contains high concentrations of organic matter, sulfates and chlorides, and the conductivity of the waste liquid in the pickling process reaches 75mS/cm.
(4) Electroplating wastewater: Electroplating plants often produce a large amount of waste liquid, although complex treatment steps such as acidification, chemical harmlessness, sedimentation and separation of sludge are adopted, and the salt content of the produced water is high and cannot be reused.
(5) Papermaking wastewater: In the pulp and paper industry, processes such as homogenization, bleaching, and papermaking require a large amount of water. Achieving a (semi-)closed cycle of water system is the best way for pulp mills and paper mills to save water resources and reduce emissions. The production water of the traditional activated sludge method also contains some colored compounds, microorganisms, antibodies and a small amount of biodegradables, suspended solids, etc., which can only be used to make packaging paper and cannot be used for the production of higher-grade paper. In addition, this method cannot reduce the content of inorganic salts.
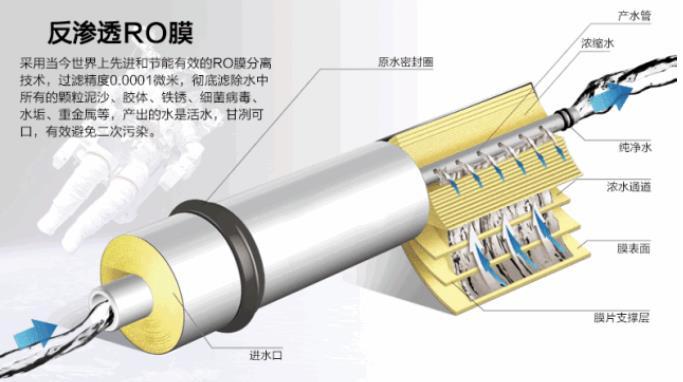
4. Reverse osmosis (RO) membrane technology
1. The principle of reverse osmosis (RO).
Reverse osmosis is a membrane separation process driven by pressure, in order to generate reverse osmosis pressure, it is necessary to use a water pump to apply pressure to the saline solution or wastewater to overcome the natural osmotic pressure and membrane resistance, so that the water can pass through the reverse osmosis membrane, and the dissolved salts or polluting impurities in the water are blocked on the other side of the reverse osmosis membrane.
2. Application of reverse osmosis membrane in water treatment
(1) Conventional application in water treatment
Water is an essential material condition for people's survival and production activities. Due to the increasing scarcity of freshwater resources, the capacity of reverse osmosis water treatment units in the world has reached millions of tons per day.
(2) Application in urban sewage
At present, the application of reverse osmosis membrane in the deep treatment of urban sewage, especially the secondary effluent reuse and reclaimed water reuse of sewage treatment plants, has been highly valued.
(3) Application in heavy metal wastewater treatment
The conventional treatment method of heavy metal ion wastewater is only a kind of pollution transfer, that is, the heavy metals dissolved in the wastewater are converted into precipitation or easier to treat, and their final disposal is often landfilled, and the hazard of secondary pollution caused by heavy metals to the groundwater and surface water environment still exists for a long time.
(4) Application in oily wastewater
Oily wastewater is a large and wide area of industrial wastewater, if directly discharged into the water body, it will produce an oil film on the surface of the water body to prevent oxygen from dissolving into the water, resulting in hypoxia, biological death, foul odor in the water, and seriously polluting the ecological environment.
5. Dialysis membrane technology
1. Various dialysis membrane technology principles
(1) Dialysis: Dialysis (D) is the process of solute transfer from the upstream of the membrane to the downstream of the membrane under the action of its own concentration gradient. Dialysis is the earliest membrane separation technology discovered and studied, but due to the limitations of its own system, the dialysis process is slow, inefficient, and the selectivity of the dialysis process is not high, so the dialysis process is mainly used to remove low molecular weight components in solutions containing a variety of solutes, such as hemodialysis, that is, the dialysis membrane is used instead of the kidney to remove toxic low molecular weight components such as urea, creatinine, phosphate and uric acid, so as to alleviate the condition of patients with kidney failure and uremia.
(2) Electrodialysis: Electrodialysis (ED) is under the action of a direct current electric field, with potential difference as the driving force, using the selectivity of the ion exchange membrane to the anions and cations in the solution, to separate the electrolyte from the solution, so as to achieve the concentration, desalination, purification and purification of the solution.
(3) Inverted electrodialysis (EDR): According to the ED principle, every certain time (generally 15~20min), the positive and negative electrode polarities are reversed with each other, which can automatically clean the dirt formed on the surface of the ion exchange membrane and electrode to ensure the long-term stability of the working efficiency of the ion exchange membrane and the quality and quantity of fresh water. In the late 80s of the 20th century, the use of inverted electrodialysis greatly improved the current and water recovery rate of electrodialysis operation, and extended the operation cycle. EDR is particularly unique in wastewater treatment, with concentrated water circulation and water recovery rates of up to 95%.
(4) Liquid film electrodialysis (EDLM): Liquid film electrodialysis is to replace the solid ion exchange membrane with a liquid membrane with the same function, and its experimental model is to use semi-permeable cellophane to wrap the liquid film solution into a thin layer separator, and then load it into the electrodialysis machine for operation. Liquid membranes using extractants as liquid membrane electrodialysis may find efficient separation methods for the concentration and extraction of precious metals, heavy metals, rare metals, etc., because finding membranes with special selectivity for certain forms of ions is related to improving the extraction efficiency of electrodialysis. It is very promising to improve the separation efficiency of electrodialysis and directly combine it with liquid membranes. For example, when the solid ion exchange membrane performs electrodialysis on the salt solution of platinum group metals (osmium, ruthenium, etc.), metal dioxide precipitation will be formed on the membrane, which will cause premature loss of the membrane and destroy the entire process.
(5) Packed bed electrodialysis (EDI): Packed bed electrodialysis (EDI) is a new water treatment method that combines electrodialysis and ion exchange method, and its biggest feature is that it uses the H+ and OH- generated by water dissociation to automatically regenerate the mixed bed ion exchange resin filled in the freshwater chamber of the electrodialysis, so as to achieve continuous deep desalination. It concentrates the advantages of electrodialysis and ion exchange methods, improving ultimate current density and current efficiency. Filler bed electrodialysis technology is highly advanced and practical, and has broad application prospects in electronics, medicine, energy and other fields, and is expected to become the mainstream technology of pure water manufacturing.
(6) Bipolar membrane electrodialysis (EDMB): Bipolar membrane is a new type of ion exchange composite membrane, which is generally composed of a cation exchange membrane laminated together, which is immediately decomposed into H+ and OH- through the water molecules of the membrane, which can be used as a supply source of H+ and OH-. The outstanding advantages of bipolar membrane electrodialysis are simple process, high energy efficiency, and low waste emissions. At present, the main application field of bipolar membrane electrodialysis process is acid-base preparation. For example, the biventricular membrane composed of bipolar membrane and positive membrane can realize the conversion of organic acids (sodium gluconate, sodium coulate, etc.), and obtain alkali (NaOH) at the same time, but the concentration (maximum concentration of acid 2mol· L-1, the maximum alkali concentration is 6mol· L-1) and purity. The current development of application fields include exhaust gas desulfurization, ion exchange resin regeneration, and inorganic processes of potassium and sodium.
(7) Electrostatic hydroelectrodialysis: Electrostatic hydroelectrodialysis is an improved form of traditional electrodialysis, and its main feature is that it removes the polar chamber and polar water of traditional electrodialysis. For example, the electrodes of the device are close to one or more layers of ion exchange membranes, which are electrically connected to each other, which can not only prevent metal ions from entering the ion exchange membrane, but also prevent the plates from fouling, and extend the service life of the electrodes. Due to the cancellation of the pole chamber and the discharge of electrodeless water, the utilization rate of raw water is greatly improved. Electrodeless hydropower dialysis came out in 1991, and the technology has been continuously improved in the application process, and the current device mostly adopts the form of frequent inverted pole in the operation mode. At present, the electrodialyzer of electrodialysis has been used in 20 provinces and cities in China, and has recently been exported to Southeast Asia.
2. Application of dialysis membrane
(1) Industrial wastewater treatment
Electrodialysis can be used for the treatment of electroplating wastewater, heavy metal wastewater, etc., extracting metal ions in wastewater, etc., which can not only recycle water and useful resources, but also reduce pollution emissions. Wan Shigui et al. studied the feasibility of passivation solution treatment in the copper production process, and found that not only the copper and zinc in it can be recovered, but also Cr3+ can be oxidized to Cr6+ and the passivation solution can be regenerated. The process of electrodialysis combined with ion exchange to recover heavy metals and acids from pickling waste has been applied in industry.
(2) Drinking water and process water treatment
In our country, electrodialysis is used to produce salt from salt spring brine in southwest China, so that the content of NaCl is stably increased to 120g/L, which increases the yield and reduces the cost compared with the original simple salt boiling method.
(3) Food industry
The most critical part of grasping the quality in the production of liquor is blending, and the quality of blending water is very important, which not only affects the internal quality of liquor, but also affects the appearance quality of liquor.
(4) Biochemical industry
A high-performance ion exchange membrane was used to separate and purify N-acetyl-L-cysteine by electrodialysis desalting method, and satisfactory results were obtained. According to the characteristics of the bipolar membrane electrodialysis system, that is, the positive membrane of the bipolar membrane precipitates H+, and the negative membrane precipitates OH-, the bipolar membrane electrodialysis technology can be applied to the separation of soybean protein, which has many advantages: the whole production process does not need to add acids and alkalis, resources can be recycled, water consumption is less, and the salt content in the isolated protein is significantly reduced.
6. Forward osmosis (FO) technology
1. The principle of forward osmosis (FO).
The solvent molecules will spontaneously pass through the membrane from the solvent side into the solution side under the action of osmotic pressure, which is the phenomenon of osmosis, which is the so-called "forward osmosis".
2. Application of forward osmosis membrane in water treatment
(1) Wastewater treatment
The application of FO in the field of wastewater has been reported in many literatures, mainly including the concentration of early high-concentration industrial wastewater, the treatment of landfill leachate, the treatment of domestic sewage, the concentration of sludge anaerobic digestate in municipal sewage treatment plants, and the life support system for directly treating sewage into drinking water on the space station. Although the FO process in these studies is not a terminal process, it has high desalting performance in the pretreatment stage. In recent years, with the continuous development of FO technology, it has attracted the attention of many scholars, and its combination with traditional membrane separation technology has become a research hotspot in recent years.
(2) Deep purification of water quality
With the development of reclaimed water reuse technology, the most successful application of FO in drinking water purification should be the direct treatment of domestic sewage generated into drinking water in the space station.
(3) Seawater desalination
In the FO system, similar to RO, the water molecules in the feedstock liquid penetrate through the semi-permeable membrane to the permeable side of the membrane, trapping the salt solution on the other side of the membrane. Therefore, the use of FO as a desalination process and method has always been the focus of researchers' research, and there are many patents at present.
03 Problems in the current membrane treatment technology
Membrane treatment technology is a new type of membrane treatment technology, with high efficiency, good operation characteristics, in sewage treatment has a good effect, membrane treatment technology is to use the selection of membrane permeability to separate water and pollutants, and finally achieve the effect of removing pollutants and purifying sewage, membrane treatment technology has the following benefits: physical and chemical technology or biological technology in the treatment of sewage its properties will change, water quality will also change, membrane treatment technology in the treatment of sewage when the properties will not change , effectively ensuring the water quality after sewage purification. Many sewage treatment methods need to add some chemical drugs when carrying out sewage treatment, membrane treatment technology does not need to add agents when carrying out sewage treatment, its own pore size and selective permeability can easily achieve the separation of pollutants, membrane treatment technology can well separate some small substances when carrying out sewage treatment, in the sewage treatment area is not large, the treatment effect is very good.
Although sewage treatment technology has great advantages over other treatment methods, there are still many problems in the actual operation, if you do not pay attention to the regular replacement of the membrane when treating sewage, long-term use will cause the membrane pores to be blocked, the membrane itself will also be polluted by pollutants, and the effect of treating sewage will be reduced. In order to make the membrane treatment technology play a key role in the treatment of sewage, it is necessary to pay attention to the timely replacement of the membrane when carrying out sewage treatment, and also pay attention to strengthening the study of water quality conditions, using comprehensive methods to treat sewage and improve the speed of membrane treatment.
















 1、超滤(UF)原理
1、超滤(UF)原理





